- Parameter
- Related products
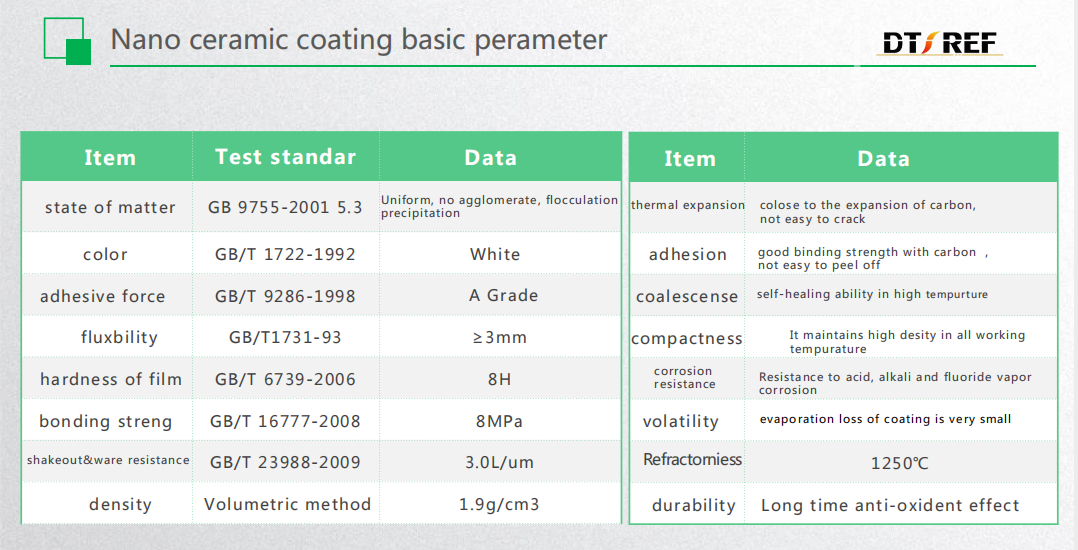
Parameter

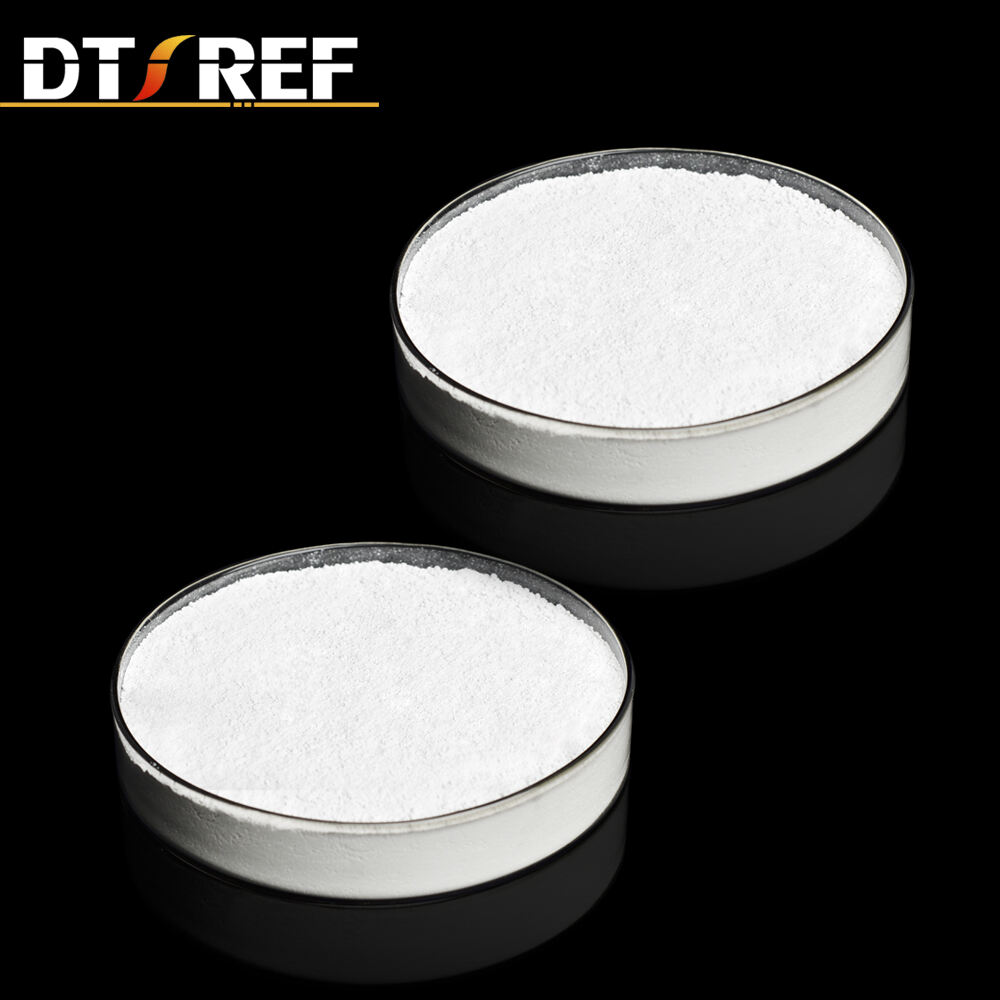
High temperature anti-oxidation nano-ceramic coating
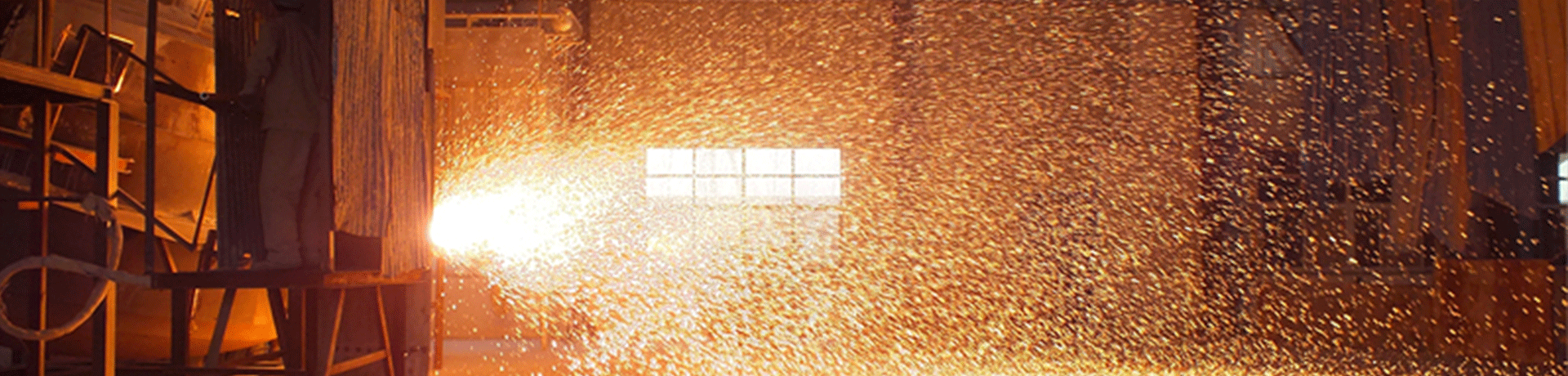
The use of high temperature protective coating technology can reduce the primary oxidation burn loss by more than 90%, greatly improve the yield of steel in the production process, directly reduce the difficulty of removing iron oxide scale, alleviate the phenomenon of surface element depletion, and improve the yield and quality of steel. Therefore, the research and application of multi-functional high-temperature protective coating technology has more important practical significance in the aspects of anti-oxidation, anti-decarburization, anti-element depletion and improvement of descaling level and rolled surface quality of high value-added steel grades.
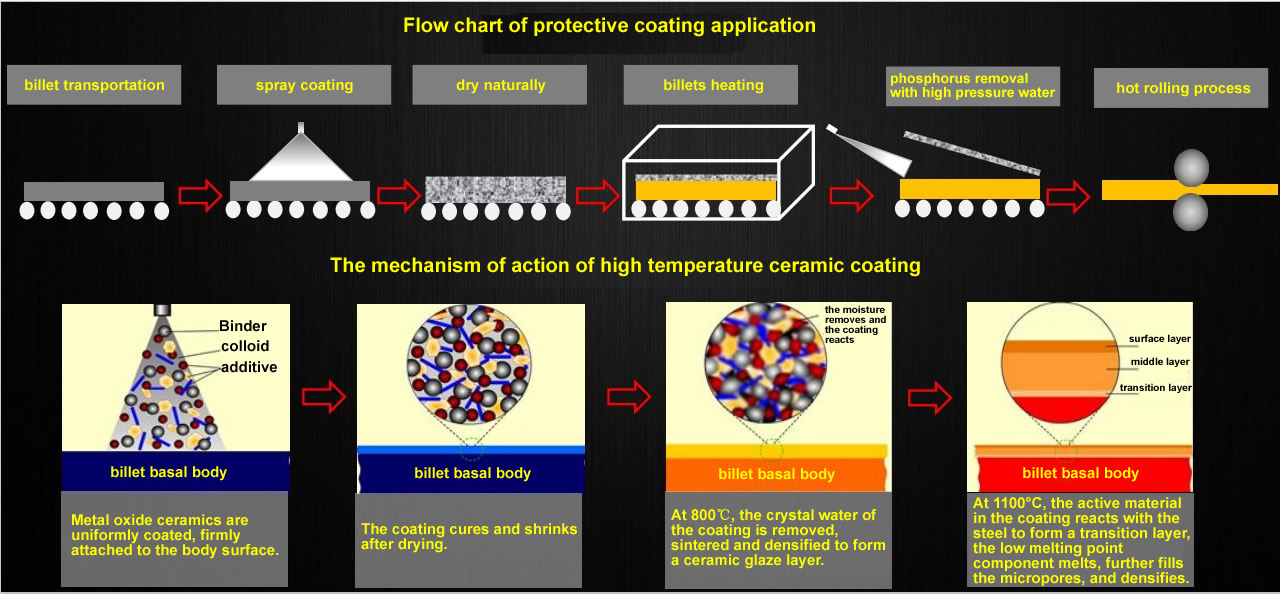
Characteristics of high temperature anti-oxidation nano-ceramic coating
1. The coating can reduce the surface oxidation of the billet by more than 90%, greatly reducing the element depletion;
2. Good chemical compatibility, mechanical compatibility, and CTE (coefficient of thermal expansion) matching between the coating and the substrate and between the inner layer of the coating and the layer;
3. The coating is closely combined with the substrate during the transmission of the steel, and the mechanical action will not cause the coating to fall off at high temperature;
4. The existing oxide layer on the surface of the coating and the steel substrate forms a new dense eutectic, which changes the structure of the oxide layer and improves the peeling performance of the oxide scale;
5. The amount of coating is small, which does not affect the normal heating speed of the billet;
6. The coating can automatically heal the cracks generated by itself in the high temperature process, ensuring the compactness and integrity of the coating;
7. The coating itself has anti-oxidation performance and long protection life;
8. The cost of coating is low. The existing anti-oxidation coatings for special steels are relatively expensive, while for ordinary low-carbon steels used in a large number of applications, these coatings are not practically applied, because of high cost.
Adverse effects of high temperature oxidation
During the heating process of rolling steel, the oxidation burning loss accounts for about 1-1.5% of the weight of the blank, and the forging heating burning loss will be higher, and the burning loss rate is as high as 3-5%.
When the furnace gas or furnace temperature is improperly controlled or the billet stays in the high temperature section for a long time, especially if the rolling failure occurs and the adjustment is not timely, the iron oxide scale of the steel will be thickened. In general, it is 1-5mm, and in severe cases, it can reach 10mm.
If the iron oxide scale produced by high temperature oxidation is not cleaned up in time, it will be pressed into the surface of the billet during the rolling or forging process, resulting in surface defects of the product. cause the product to be scrapped. When heating steel parts, high-temperature oxidation will also cause depletion and decarburization of alloying elements in the steel, and changes in the chemical composition of the steel surface will cause production. The mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the product decrease, resulting in a decrease in the qualified rate of the finished product.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR HR
HR CS
CS DA
DA NL
NL FR
FR DE
DE EL
EL HI
HI IT
IT JA
JA KO
KO NO
NO PL
PL PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES SV
SV TL
TL ID
ID LT
LT SR
SR SK
SK UK
UK VI
VI HU
HU TH
TH TR
TR MS
MS GA
GA CY
CY AZ
AZ LO
LO LA
LA MN
MN NE
NE MY
MY KK
KK UZ
UZ